Introduction
Hearing is one of the most important senses, playing a crucial role in communication, learning, and overall quality of life. Ear health encompasses not only the physical structure of the ear but also the proper functioning of the auditory system, including the outer, middle, and inner ear. Maintaining healthy hearing requires a combination of preventive measures, early detection of issues, and understanding potential risks such as prolonged exposure to loud noises, infections, or age-related changes. A comprehensive approach to ear care involves regular check-ups, awareness of environmental and lifestyle factors, and proper hygiene practices. By understanding the fundamentals of ear health, individuals can take informed steps to preserve their hearing, prevent avoidable damage, and respond appropriately if problems arise.
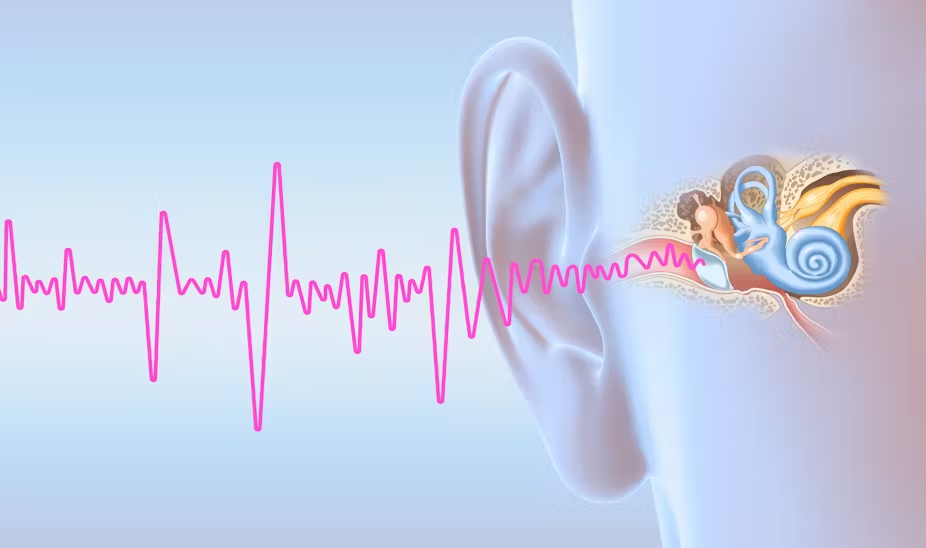
1. Understanding the Structure of the Ear
The ear consists of three main parts: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. The outer ear captures sound waves and directs them into the ear canal, where they reach the eardrum. The middle ear contains tiny bones called ossicles that transmit vibrations to the inner ear. The inner ear includes the cochlea, which converts sound vibrations into nerve signals sent to the brain. Understanding this structure helps explain how hearing works and why protecting each part is essential.
2. Common Risk Factors for Hearing Damage
Hearing loss can result from multiple factors, including exposure to loud sounds, ear infections, aging, genetic predisposition, or certain medical conditions. Occupational noise, frequent use of headphones at high volume, and environmental noise pollution are common contributors. Awareness of these risks allows individuals to take preventive actions.
3. Preventive Measures
Preventive measures are key to maintaining healthy hearing. These include avoiding prolonged exposure to loud noise, using hearing protection in noisy environments, keeping ears dry and clean, and limiting insertion of objects into the ear canal. Regular hearing assessments, especially for those in high-risk environments or older adults, can detect early changes in hearing ability.
4. Recognizing Early Signs of Hearing Problems
Early detection of hearing issues can significantly improve outcomes. Common warning signs include difficulty understanding conversations in noisy environments, frequently asking others to repeat themselves, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), or a gradual decline in hearing sensitivity. Consulting a qualified healthcare professional when these symptoms occur is essential for timely evaluation and management.
5. Professional Care and Treatment Options
Ear specialists, or audiologists and otolaryngologists, provide diagnostic testing, monitoring, and treatment for hearing problems. Interventions may include medical management of infections, hearing aids, assistive listening devices, or rehabilitation programs. Early intervention can prevent further deterioration and support effective communication.
Summary
Maintaining ear health is critical for overall well-being and effective communication. By understanding the ear’s structure, recognizing risk factors, practicing preventive measures, and seeking professional care when necessary, individuals can protect their hearing and enhance their quality of life. Regular attention to ear health, combined with awareness of environmental and lifestyle influences, forms the foundation for lifelong auditory wellness.